The amount of contaminated water laced with raw sewage that is flowing across the U.S.-Mexico border into San Diego County exceeded 44 billion gallons in 2023, the most on record in the last quarter-century, https://phys.org/news/2024-07 reports said.
And this year’s volumes could surpass all records should the region get more damaging rainstorms.
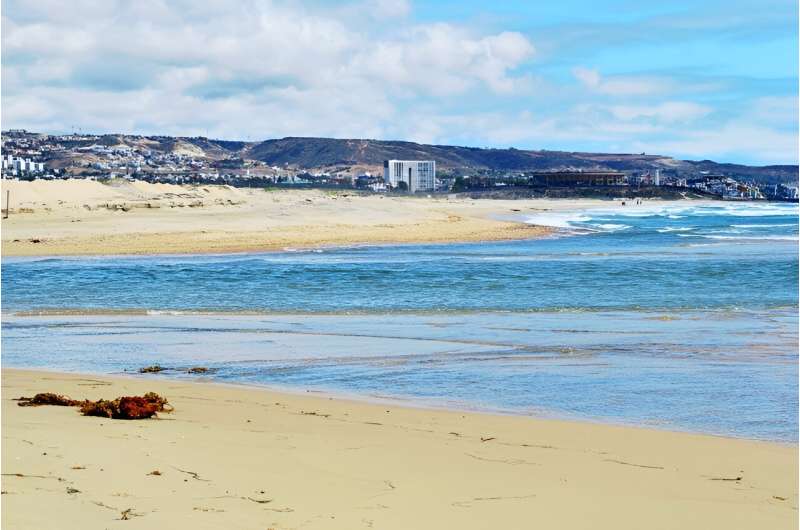
As of June, the U.S. International Boundary and Water Commission (USIBWC) has recorded 33.55 billion gallons of polluted water, or flows, in the river, which makes its way into the Tijuana River Valley and the Pacific Ocean. That’s enough water to fill 50,800 Olympic-size swimming pools.
Flows are comprised of stormwater, groundwater and raw sewage. Rainstorms in the past couple years have brought staggering amounts of that polluted stew over the border into San Diego County, flooding some South Bay roads where people have had to be rescued, extending beach closures, and bringing sedimentation and trash to the Tijuana River Valley.
A Jan. 22 storm filled a north levee near the South Bay International Wastewater Treatment Plant with more than 1,100 tons of debris. The IBWC finished cleaning it up in late May.
The data was presented during a USIBWC Citizens Forum meeting, where agency officials gave updates on wastewater infrastructure projects on both sides of the U.S.-Mexico border that are expected to reduce the amount of untreated wastewater in the river.
On the U.S. side, the IBWC is focused on repairing and expanding the South Bay plant. The 1997 facility has not been properly maintained for decades and is noncompliant with its Clean Water Act discharge permit.
But it should reach compliance by next month, officials said. To get there, several parts that have been inoperable for years are being repaired or replaced.
For example, all five of the plant’s primary sedimentation tanks, which separate solids from the flow, were down since March 2023. Two are now running and a third is expected to come online next week, said Morgan Rogers, the plant’s area operations manager. A minimum of three is required for its permit and all five should be operational by September.
The facility also has most of its influent pumps running again, after Tropical Storm Hilary broke five of six. It had no spares. These pumps, costing about a half-million dollars each, serve as the entryway into the facility’s treatment process. Four new pumps have been ordered, three of which will be spares, said Rogers.
“We were down to one pump because of all the excessive flow and trash and sediment that came through,” he said. “This is critical. We almost shut the plant down.”
The August 2023 storm also took out all four of Hollister Pump Station’s pumps, located on Hollister Street near Monument Road where several horse ranches are based. All pumps have been replaced but the facility is still experiencing malfunctions.
In June 2024, a pressure relief valve on a surge tank stuck open, causing hundreds of thousands of gallons of wastewater to spill onto Hollister Street. Rogers said sediment buildup caused the valve to fail. Hollister remains out of service with no flows going through it while the agency works to replace the tank.
At the same time, the agency is trying to double the South Bay plant’s capacity as part of a major plan to reduce cross-border pollution. The IBWC expects to award a construction contract sometime August 2024. Even with more than $400 million Congress has allocated to the agency to date, officials estimate a shortage of about $200 million for the expansion project.
On the south side of the border, the Mexican military is rebuilding a defunct sewage treatment plant in Baja California that has discharged 40 million gallons of wastewater per day into the ocean. Mexican officials said the plant will be ready by the end of September or early October.
“We think that’s pretty aggressive,” said Rogers. “Hopefully, we’re on schedule. We’ll see some improvement in the water quality in the ocean down south.”
Construction on the pipeline should be completed this summer, officials said.
The juggling act of fixing longstanding issues and repairing new malfunctions has many South County residents and environmentalists questioning when they’ll find relief from pollution, which has compromised public health, the environment and the economy on both sides of the border.
San Diego Coastkeeper Executive Director Phillip Musegaas is among them. He attended Wednesday’s Citizens Forum.
“We’re appalled,” he said. “This is outrageous that we’ve had this little progress over this amount of time despite the large infusion of federal funding that we’ve seen over $400 million in the past three years. We need to see more progress.”
Coastkeeper and the Coastal Environmental Rights Foundation are suing the binational agency over water-quality permit violations for discharging “pollutants such as fecal bacteria, contaminated sediment, heavy metals, and toxic chemicals” into the ocean.
On the federal side, San Diego’s Congressional delegation is pushing to add more funds to cover the South Bay plant costs by asking several federal entities to pitch in, such as the Department of Homeland Security, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Services, the Environmental Protection Agency and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Rep. Scott Peters is also working to secure hazard pay for Border Patrol agents working in polluted waters. And the state Assembly is considering a bill from state Sen. Steve Padilla that would require multinational companies doing business in California to reduce their wastewater discharges or face penalties.