A multi-institutional team of animal behaviorists, snow impact specialists and biologists from Alaska, Montana, Switzerland and Canada has found that large numbers of wild mountain goats die every year in Alaska due to avalanches. For their study, the group tagged hundreds of wild mountain goats over 17 years across Alaska. Their findings are published in the journal Communications Biology, https://phys.org/news/2024-05 reported.
An avalanche occurs when snow resting on a sloped part of a mountain suddenly slides downhill en masse. The force of the moving snow is far too great for animals or humans to overcome. Victims in the path of an avalanche can be killed by the impact of the snow, which crushes them, or by being buried and unable to dig themselves out. In this new study, the researchers noted that little work has addressed the impact of avalanches on wild animals, particularly those that are suspected of being most at risk, such as wild mountain goats.
Wild mountain goats are known for their risky behavior—they climb on cliff faces, seemingly attempting to defy gravity. Prior research has shown that they do so to evade predators and to lick the rocky cliff face as a means of ingesting salts and other minerals. This behavior, the researchers note, would seem to put the goats at risk of falling victim to avalanches.
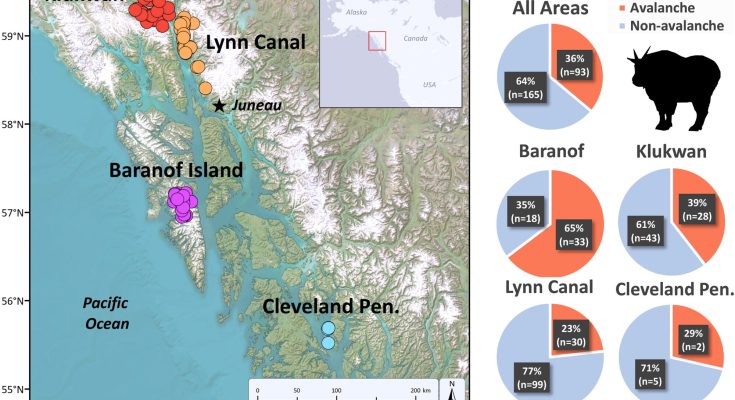
To investigate, the researchers captured, tagged and tracked 421 goats over a 17-year period. When a goat stopped moving, indicating it had died, the team went into the field to find out the reason. This way they were able to compare the number of deaths due to avalanches to deaths by other means, such as predation, falling off cliff faces, or disease.
The research team found that death by avalanche was common for the goats—in one region, it was responsible for 65% of deaths. They found that overall, approximately 8% of all wild mountain goat deaths in Alaska were due to avalanches—a percentage they describe as significant.